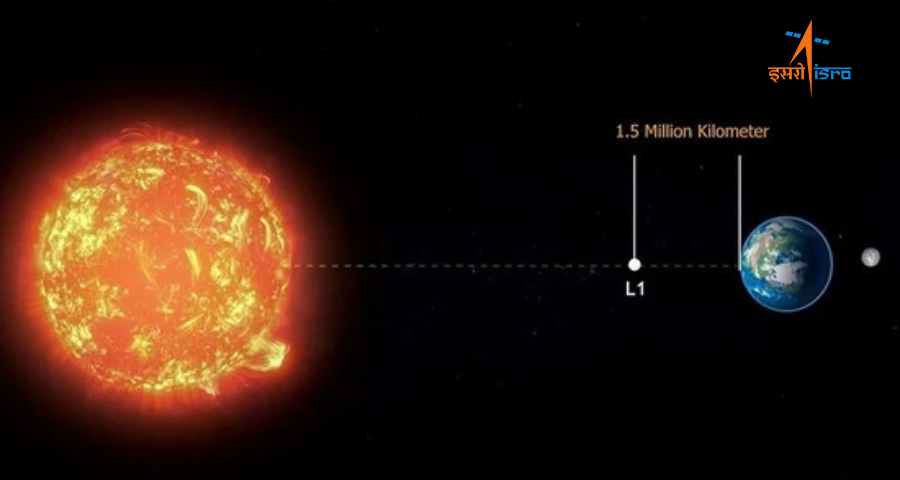
On September 2, 2023, India successfully launched its inaugural solar mission, Aditya-L1, from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota. The spacecraft flawlessly achieved orbit around the Sun-Earth Lagrange Point 1 (L1), situated approximately 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
Aditya-L1 serves as a solar observatory primarily dedicated to the study of the sun’s corona, the outermost layer of the sun’s atmosphere. The spacecraft is outfitted with a suite of instruments designed to measure the sun’s magnetic field, solar wind, and various other properties.
The Aditya-L1 mission is the result of a collaborative effort between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the European Space Agency (ESA). The ESA contributed the spacecraft’s payload module, housing the scientific instruments.
The successful launch of Aditya-L1 marks a significant milestone for India’s space program as it represents the nation’s maiden mission dedicated to solar exploration. Furthermore, this mission promises to enhance our comprehension of the sun’s impact on Earth’s climate and weather patterns.
Additionally, the Aditya-L1 mission underscores the deepening cooperation between ISRO and ESA, who have previously joined forces on various missions, demonstrating their commitment to continued collaboration.
The Aditya-L1 mission ISRO is anticipated to endure for at least 5 years. Over this span, the spacecraft will amass a wealth of data pertaining to the sun. This data will be instrumental in refining our understanding of the sun’s behavior and its repercussions on Earth.
The triumph of the Aditya-L1 mission is a remarkable feat not only for India and ESA but also for the dedicated scientists and engineers who tirelessly contributed to its realization. It stands as a testament to the burgeoning partnership between these two esteemed space agencies.
The Advantages of the Aditya-L1 Mission
The Aditya-L1 mission holds numerous benefits for India and the global community, including:
- Enhanced Sun Understanding: The Aditya-L1 mission’s data collection efforts concerning the sun’s corona, magnetic field, and other attributes will significantly advance our comprehension of the sun’s characteristics and its influence on Earth.
- Improved Space Weather Forecasting: This mission will bolster our capacity to forecast space weather phenomena such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, events that can disrupt terrestrial communications and power grids.
- Advancement of Solar Technologies: Insights gathered from the Aditya-L1 mission will facilitate the development of novel solar technologies, including solar power systems and solar sails.
- Augmented International Collaboration: By uniting ISRO and ESA in a collaborative endeavor, the Aditya-L1 mission serves as a catalyst for strengthening the bonds between these two space agencies and promoting international cooperation within the realm of space exploration.
The Future of Solar Exploration
The launch of the Aditya-L1 mission marks the initial step in India’s burgeoning solar exploration initiative. ISRO has outlined plans to launch several more solar missions in the forthcoming years, including Aditya-II, Aditya-III, and Aditya-IV. These missions will persist in scrutinizing the sun and its interactions with Earth.
Moreover, the Aditya-L1 mission underscores the growing significance of solar exploration. Given that the sun is the ultimate source of life on our planet, comprehending its conduct is paramount. The Aditya-L1 mission, with its wealth of data, paves the way for future solar exploration endeavors.
Also Read: EVERYTHING THAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT CHANDRAYAAN 3
Conclusion
The triumphant launch of the Aditya-L1 solar mission is a monumental achievement, symbolizing India’s burgeoning capabilities in space exploration and highlighting the robust partnership between ISRO and ESA.
This mission is poised to bring about a multitude of advantages for both India and the global community. It will deepen our knowledge of the sun, enhance space weather forecasting, foster technological innovation, and promote international collaboration in space exploration.
India’s commitment to solar exploration is just commencing with the Aditya-L1 mission, and the nation’s plans for future solar missions promise to further our comprehension of the sun and its implications. The Aditya-L1 mission is an extraordinary leap forward in our pursuit of solar knowledge and underscores the remarkable progress in India’s space program.